The information that you need to be aware of when it comes to vitamin D supplementation for your entire family.

This blog post was written in paid partnership with Webber Naturals. As always, the opinions are my own!
I have no doubt that you’ve heard about the importance of vitamin D (aka the sunshine vitamin) for proper health. And for good reason! As a registered dietitian my nutrition philosophy is very much grounded in a “foods first” approach, with one exception: Vitamin D. In this blog post I’m going to explain why that is, and why it’s so important to include daily vitamin D supplementation for each family member, no matter what age, stage, or time of year.
Vitamin D supplementation is super important—from pregnancy, to infancy, to childhood, into adulthood—for multiple reasons. If you’re wondering what vitamin D is, where it comes from, why it’s important for your health, and why Canadian families should be making it a priority to take a supplement daily, read on!
Here’s what I’ll cover:
- What is vitamin D and why is it important?
- How much should everyone in the family get (by age)
- Why you will not get enough from sun exposure (especially living in Canada)
- Can you get vitamin D through food (and a comparison of foods and supplements to demonstrate this)

First of all, what exactly is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble, essential nutrient that we require for health. Being “fat-soluble” means that dietary fat is required for its absorption into the body. It is also classified as an essential nutrient because, although a small amount of it can be made in the body with the help of the sun (read more on this below), we don’t make enough to satisfy our requirements. This is why it is recommended to take daily vitamin D supplements.
Vitamin D is essential for proper health, for many reasons. It helps your body use calcium and phosphorous in order to maintain strong bones and teeth (which is especially important for our little ones), and it has been linked to improved immune function (which is top of mind for everyone right now). Vitamin D increases the body’s production of proteins that kill viruses. A landmark meta-analysis published in the British Medical Journal in 2017 looked at 25 studies on vitamin D and respiratory infections (coughs and colds).[i] Researchers found that taking vitamin D supplements can protect against respiratory infections.
Vitamin D may also help to reduce your risk of certain chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and certain cancers (especially colorectal cancer).

How much does everyone need?
Prenatal:
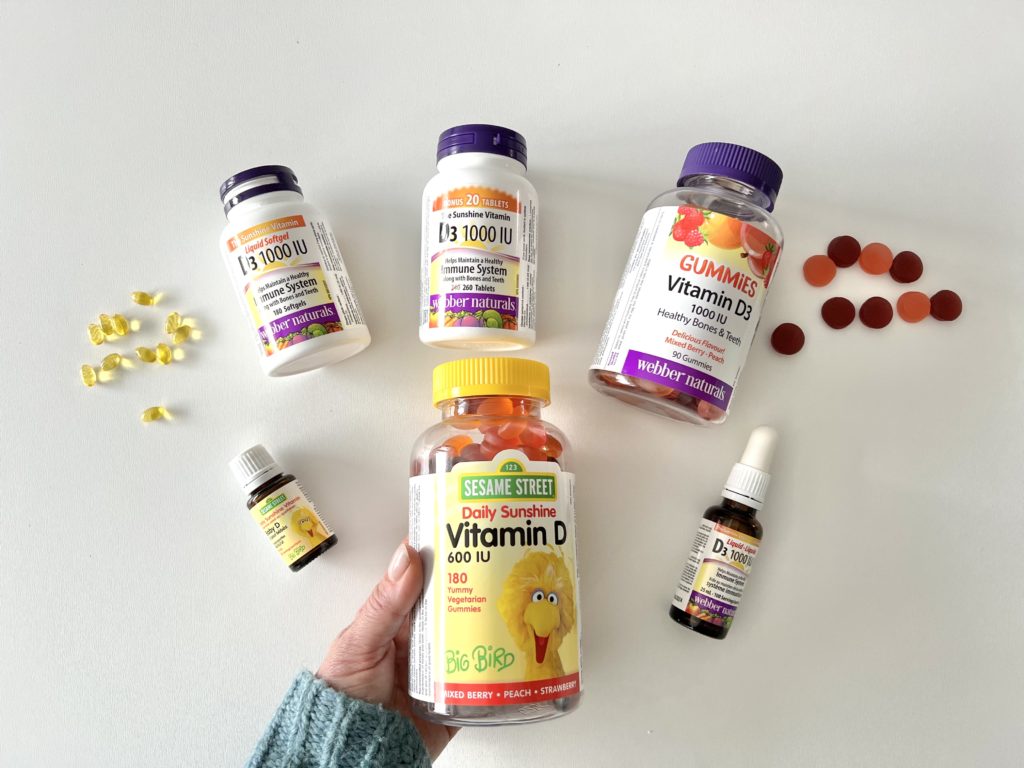
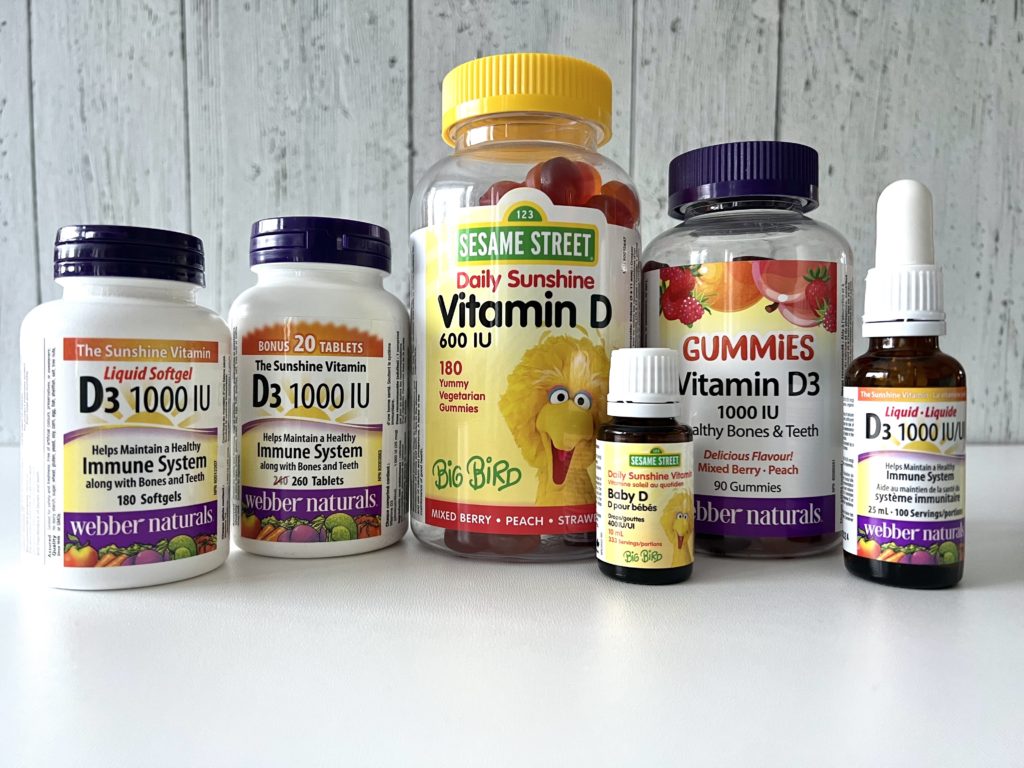
If you are expecting a baby, vitamin D supplementation is very important. After all, you’re supporting your growing baby’s nutritional needs and your own as well. The recommended amount of vitamin D during pregnancy is 600 IU per day, but most health experts (like me) suggest taking an additional 1,000 IU of vitamin D (my fave is the Webber Naturals 1,000 IU Vitamin D Gummies because they are a fun and convenient way to get the right amount of vitamin D for the day, and great for those looking for an alternative to the tablet form), in addition to your prenatal multi.
Post-partum:
Vitamin D is very important for new moms in the post-partum period. When it comes to post-partum healing, there’s a link between pelvic floor muscle strength and higher vitamin D status.[ii] There’s also a link between low vitamin D status and a higher probability of post-partum depression.[iii] And we already know that vitamin D also helps with calcium absorption and bone health. For these reasons (plus more), I recommend that new moms continue to take their pre-natal multivitamin during that first year post-partum as WELL as a vitamin D supplement of at least 1,000 IU daily.
Infants:
Typically, you don’t have to worry about nutritional supplements for your baby, again, with the exception of vitamin D, which is a must for breastfed babies (and formula-fed babies consuming less than 32 ounces per day).

Breastfed babies:
Breastmilk doesn’t provide much vitamin D, and because vitamin D is so important for preventing rickets (the softening and weakening of bones in children) a supplement is necessary.
It’s not recommended to give more than about 400 IU per day—anything over 1,000 IU per day, for an infant 6 months and younger is too much, and can put baby at risk of vitamin D toxicity.
Formula-fed babies:
When it comes to formula-fed babies, if you’re feeding your baby less than 32 ounces (4 cups) of fortified infant formula a day, you should be giving your baby 400 IU of liquid vitamin D a day—starting in the first few days after birth. Continue giving your baby vitamin D until they reach 32 ounces (4 cups) of formula a day. Once your formula-fed baby has started solids and is consuming less formula, you can introduce the 400 IU vitamin D supplement again and continue throughout childhood.
Liquid vitamin D drops are what is recommended at this age and stage (my preferred choice being Webber Naturals Sesame Street Baby D Drops as the liquid vitamin D formula is made especially for infants 0 and up). They are SO easy to use: you just apply 1 droplet (yes, just one – each drop contains 400 IU of vitamin D3 in a base of organic flaxseed oil to ensure proper intake every day) to your nipple (or the bottle’s nipple) before baby latches on, and they ingest it while they feed. You can also apply the drop to your clean finger and let baby lick it off.

Toddlers:
Your toddler’s vitamin D requirements jump from 400 IU per day to 600 IU per day. Even with the addition of cow’s milk (if you choose to serve milk), vitamin D supplementation needs to continue. It’s very difficult to meet requirements through food alone, since few foods contain vitamin D. Continue with a 400 IU supplement daily, the Baby D drops still work well during this period.
Children and teens:
Kids aged 3 and up require 600 IU of vitamin D per day, so Webber Naturals Sesame Street Daily Sunshine Vitamin D gummy works really well. My kids love it because it feels like a treat, and I love it because they only require one gummy a day (not multiple). This gummy is appropriate from ages 3-17.

Young adults and parents:
The daily recommended intake of vitamin D for adults (up to age 71) is 600 IU per day, but most experts agree that 1,000 – 2,000 IU per day in supplement form is best. Webber Naturals has a few options and various forms of vitamin D supplements. If your older teen or young-adult-aged child prefers to take a liquid supplement or a pill-form supplement, they can graduate to Webber Naturals Liquid D3 , which offers 1,000 IU per dose, or the liquid D3 Softgels or Tablets which also offer 1,000 IU per dose.
I personally take two of Webber Naturals Vitamin D3 Gummies a day (which equals 2,000 IU per day). The nice thing is you don’t have to worry about pairing it with food or taking it at a certain time every day. Just whenever it works best for you!
What about if some (or all) of our family members are vegetarian or vegan?
Low serum vitamin D concentrations have been found with vegetarian children, so it’s an important nutrient to watch, especially in the winter months in Canada. Few foods contain vitamin D—the short list is fish (which vegetarians don’t eat), dairy (which vegans don’t eat), and some mushrooms (which people don’t tend to eat daily). I recommend vitamin D supplements for ALL kids (vegetarian or not), so this is easy advice: Get 400 to 600 IU of vitamin D daily from supplements. Webber Naturals Vitamin D Gummies (for kids and adults) are vegetarian too!
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for Vitamin D
| Age | RDA (IU) | Upper Limit (IU)* |
| 0-6 months | 400 | 1,000 |
| 6-12 months | 400 | 1,500 |
| Children 1-3 years | 600 | 2,500 |
| Children 4-8 years | 600 | 3,000 |
| Children and Adults 9-70 years | 600 | 4,000 |
| Adults over 71 | 800 | 4,000 |
| Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women | 600 | 4,000 |
* This includes from both food and supplements
Don’t we get Vitamin D from the sun?
Yes…well, sort of. When we are outside in the sun, the UV rays hit our skin, and a cascade of events happen to convert 7-dehydrocholesterol (a cholesterol precursor) under the skin’s surface into vitamin D. Neat hey? BUT! We are probably (hopefully) wearing sunscreen (and putting it on our kids!) during warm summer months. I’ve got a whole blog post on vitamin D for kids in the summer months, too. Sunscreen blocks those UV rays and therefore prevents that step in the synthesis of vitamin D3 under the skin. So, we can’t rely on sun exposure alone (especially those of us that live in northern, colder climates) for vitamin D. If you live in Canada, like me, we’re not only dealing with long, cold winter months (when we are very bundled up), but also some cloud-cover and smog, both of which affect vitamin D synthesis from sun exposure.

Can’t you get Vitamin D through food?
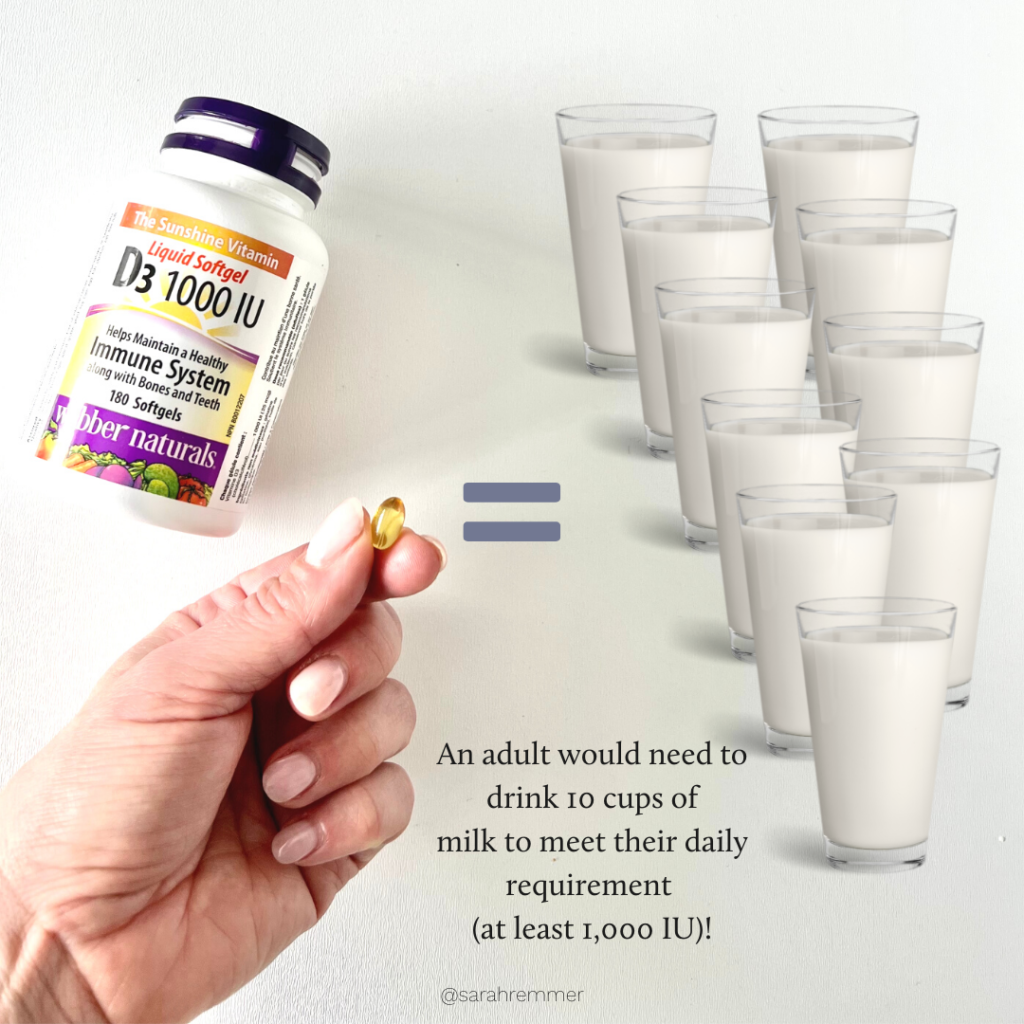
As mentioned above, there are a limited number of food sources of vitamin D. Some of them are salmon, cow’s milk, egg yolks, yogurt and margarine. But meeting your recommended daily requirements through food alone, is very difficult, if not impossible (depending on age). And in some cases, as a dietitian I wouldn’t recommend it. For example, an adult would have to consume 10 cups of cow’s milk per day and a child would have to consume 6 cups of cow’s milk per day to meet their daily requirements. This isn’t something that I would ever recommend, because although milk is nutritious, consuming too much of it can displace other important nutrients in the diet such as iron. It can also fill kids stomachs and create a bit of a battle mealtime.
Another example is eggs. Although egg yolks do contain vitamin D, an adult would have to consume over 20 eggs a day to meet their daily requirement. We all know that is just not happening, nor should it. Bottom line? Even if you and your family consumes these vitamin D-rich foods, you should still take a daily supplement.
Here are some of the top food sources of vitamin D:
| Food source | Serving size | Amount of Vitamin D (International Units, IU’s) |
| Cow’s milk | 1 cup | 100 |
| Fortified milk alternative | 1 cup | 85 |
| Plain yogurt | ¾ cup | 58-71 |
| Egg yolk | 2 large | 57-88 |
| Canned Salmon | 2.5 oz | 394-636 |
| Margarine | 1 tsp | 25-36 |
| Vit. D Fortified Orange Juice | ½ cup | 50 |
There are a lot of other common misconceptions about Vitamin D. I dispel some of the most common myths over at the Webber Naturals Blog in my post “D-Coding Vitamin D: The Top 5 Myths You Need To Know.”

Bottom line?
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient for every single member of your family, and although there are some nutritious food sources available, it’s much too hard to rely on food alone. That’s why I recommend that each family member supplement with vitamin D daily. If you’re curious about what dose to take or if you’re deficient, check with your doctor or book an appointment with a registered dietitian!
The truth is, for those of us living in Canada, daylight is short and winters are long. Webber Naturals wants to ensure you and your family has their daily dose of the “Sunshine Vitamin” during these long winter months. You can explore the wide range of vitamin D products available to support you and your family’s overall health and wellness at WebberNaturals.com.

[i] Adrian R Martineau et al., “Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections,” https://www.bmj.com/content/356/bmj.i6583.
[ii] Badalian SS and Rosenbaum PF, “Vitamin D and pelvic floor disorders in women: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey,” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20308841.
[iii] E. R. Ellsworth-Bowers and E. J. Corwin, “Nutrition and the psychoneuroimmunology of postpartum depression,” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3564601/.




![[AD] It’s Day 6 of my 15-Minute Supper Series and today we’re putting a delicious twist on a classic BLT to make it nourishing and meal-worthy 🤤
Make sure to comment “Spud” and I’ll send you my top dietitian tips for feeding your family on busy weeknights along with a huge list of meal ideas!
This pasta salad takes no time at all to throw together and has everything you need for a nourishing meal. I always make extra bacon for things like this, but if you don’t have any cooked bacon I find cooking it in the airfryer or stovetop the quickest 🥓
I find that this salad lasts 2-3 days in the fridge without getting too soggy. You can also add in fresh lettuce to crisp it up or add the dressing when you eat it.
I ordered all of my groceries from @spuddelivers, which always saves me time and effort and gives me peace of mind knowing that I’m using high-quality, local and sustainable ingredients. I love that they come straight to my door the day after ordering 🙌🏻
Let’s make it!
Ingredients:
* 10 slices bacon cooked and diced
* 12 ounces pasta cooked and cooled
* 1 cup homemade Ranch dressing
* 1 ½ cup baby tomatoes diced
* ½ avocado diced
* feta
* ⅓ cup red onion diced
* 1 cup romaine lettuce
* fresh parsley for garnish optional
Homemade ranch dressing:
* ¾ cup mayonnaise
* ½ cup sour cream or Greek yogurt
* ½ teaspoon dried chives
* ½ teaspoon dried parsley
* ½ teaspoon dried dill weed
* ¼ teaspoon garlic powder
* ¼ teaspoon onion powder
* Salt and pepper to taste
Make it:
1. Blend all Ranch dressing ingredients together in a small blender (or whisk by hand) and set aside.
2. In a large bowl assemble the pasta, tomatoes, avocado, cheese, red onion, lettuce and bacon.
3. Pour the dressing over and toss to combine.
4. Garnish with parsley and serve.
You are going to LOVE this meal-worthy salad, I promise!
Comment SPUD to receive my top dietitian-approved tips for feeding your family during the week, a long list of ideas, and a curated shopping list with all of the ingredients for this recipe + all of the other ideas that I share in this resource!
#sponsored #spuddelivers #15minutemeals #whatsfordinner #easymealideas #dietitianapproved](https://www.sarahremmer.com/wp-content/uploads/sb-instagram-feed-images/438745920_798281295514125_2547899647147267180_nfull.jpg)



Comments
Cynthia @ Activefamilychiroaz says
Vitamin D supplementation can be an effective way to ensure that you are getting enough of this essential nutrient, which is important for bone health, immune function, and overall wellbeing. While it is possible to get vitamin D from dietary sources such as fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods, some people may find it difficult to consume enough of these foods to meet their daily vitamin D needs.
Carola Jain says
Vitamin D is perhaps the most common supplement that people consume, especially since there aren’t many foods with this in high volume. Great insight shared here!
Sarah Remmer says
You’ve got it, Carola! Thanks so much.